New Delhi: On January 4, 2023, the Union Cabinet passed the National Green Hydrogen Mission that will aid in promoting the hydrogen ecosystem. Following this approval, this mission was incorporated in the Union Budget for FY24 with an allocation of INR 19,744 crore. The mission targets annual green hydrogen production of 5 MMT (million metric tonnes) by 2030, to decarbonize the industrial, mobility, and energy sectors, and to minimize the dependence on imported fossil fuels and feedstock. The following Q&A aims to clear the possible doubts about hydrogen as a fuel for commercial vehicle internal combustion engines.
Q: Why do we require zero-emission battery electric and hydrogen technology vehicles?
The transportation sector contributes 24% of direct CO2 emissions from fuel combustion, which produces 10% of greenhouse gas emissions in the world. Zero-emission technology vehicle aids in the green industrial, environmental, and economic transition.
Q: What is a hydrogen internal combustion engine (H2ICE)?
H2ICE is an engine that is tailored for commercial vehicle use which aims to minimize greenhouse gas emissions. The engine uses hydrogen as its fuel and generates near-zero carbon emissions. Interest in H2ICE has increased in recent years.
Q: What are the types of hydrogen-powered ICEs?
There are two types of hydrogen-powered engines; hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs, and H2ICE. To power the electric motors, FCEVs produce electricity from hydrogen in a device called a fuel cell. In the latter H2ICE burns hydrogen to generate the required power.
In March 2022, Tata Motors showcased its prototype of a FCEV bus and itstruck a deal with Indian Oil Corporation for 15 fuel cell buses.
Q: Who uses H2ICEs now?
Powertrain development companies use H2ICE for heavy-duty applications. It targets to increase the efficiency of multiport and utilizes the current powertrain architecture.
In February 2023, Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) in partnership with Ashok Leyland unveiled its first H2ICE technology for heavy-duty trucks. It was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in Bengaluru during the India Energy Week. Besides this, JCB has started a project of EUR 100 million to generate efficient hydrogen engines.
Q: Is H2ICE cost-intensive?
Yes, H2ICE is cost-intensive. It demands clean hydrogen and a highly specific compressor to circulate compressed air.
Q: Why Europe switch over to FCEV while India prefers H2ICE?
European countries are switching to hydrogen fuel cell commercial vehicles. This happened when the European Union government representatives came together in March 2020 at Sofitel, Brussels, to find a solution for a carbon-neutral Europe by shifting to Hydrogen FCEVs. Henrik Hololei, Director-General, DG MOVE (DG for Mobility and Transport), pointed out that a Toyota Europe survey revealed that 72% of the sample audience preferred hydrogen as an alternative fuel medium for commercial vehicles (CVs). The sample audience voted for hydrogen FCEVs.
However, India is switching to H2ICE as a minimum replacement for the conventional powertrain and vehicle system, thus making it a practical option for India, Africa, and other budget-conscious countries. It can retrofit the current ICE CV fleet, making it an easier option to choose.
Q: Has India tried making FCEVs?
In India, Tata Motors in association with ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) displayed Starbus for city operations in 2017. Also, India at that period invited global expression of interest (EoI) to supply 10 hydrogen fuel-cell-based electric buses and the same amount of fuel-cell-based electric cars in Leh Ladakh and Delhi to decarbonize the mobility sector.
TCPL Green Energy Solutions on August 25, 2023 signed a pact with the Jharkhand government to set up a manufacturing facility with an investment of INR 350 crore in the coming years to produce H2ICE, battery, and fuel cell electric vehicle systems along with fuel delivery systems.
Q: Which fuel is purest, FCEV or H2ICE?
Hydrogen FCEV is the purest. That is why the western countries opt for it. However, H2ICE is also pure compared to conventional fuels (less than 5% of pollutants). The H2ICE produces only nitrogen as a pollutant which is negligible compared to conventional fuel pollutants. The Indian OEMs have already started developing H2ICEs or are planning to develop them soon. Some major automakers have showcased their H2ICE technology at the Auto Expo 2023. Thus, both are practical options for reducing emissions to near zero.
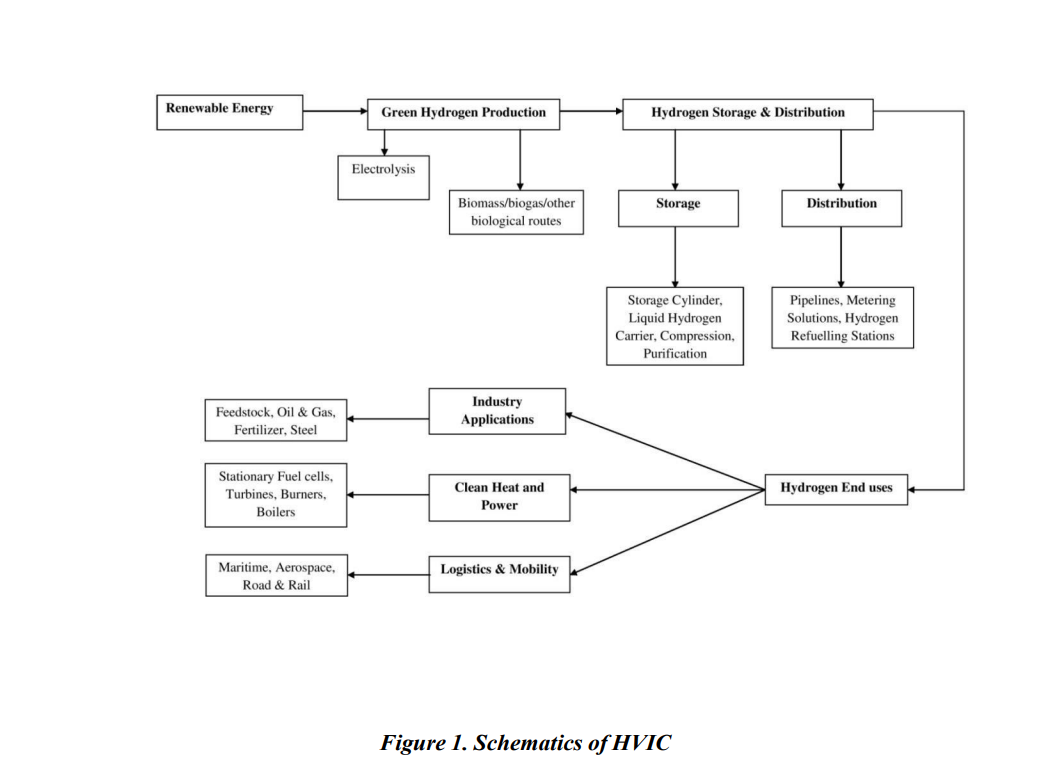
Q: What is the Hydrogen Valley Innovation Cluster?
A hydrogen valley refers to a geographical area where hydrogen is used in more than one sector or application in industry, energy, and mobility. This concept was made to foster the green hydrogen transition better by the Department of Science and Technology (MoS&T).
Its objective is to demonstrate how technology development in the value chain of hydrogen (production, storage, and transportation) in the form of an energy vector comes together in a system through which industrial deployment is possible at a small scale.
One such example of the Hydrogen Valley Innovation Cluster is Gujarat which launched the Hydrogen Valley Project in April 2023. Its stakeholders and collaboration include the Department of Science and Technology- Government of India, the Government of Gujarat, and the Office of Principal Scientific Advisor to the Government of India (only collaboration).
Q: What is the hydrogen market in India?
The Asia Clean Energy Forum, 2023, presents hydrogen demand as approximately 90 MMT/year, which is expected to grow further. The demand is anticipated to grow 2.5-3.5 times by 2040. However, it is assumed that it won’t be meeting more than 5% of the primary energy consumption of India by 2040.
India can save up to USD 15 billion to USD 20 billion annually in fossil fuel imports when it replaces fossil fuel in the end-use sectors with locally produced hydrogen. The renewable energy power requirement for green H2 will be around 400 GW.