The Latest
Temperature records continue to topple. Last month was the planet’s warmest August in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s 174-year record, agency officials said on Thursday. The global surface temperature for the month was 2.25 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1.25 degrees Celsius, above the 20th century average.
July and June also the warmest on record globally, and global surface sea temperatures hit a record high for the fifth month in a row.
In the United States, this August was the ninth-warmest on record. But Florida, Louisiana and Mississippi were especially hot, with all three states experiencing their warmest August ever.
Why It Matters: Climate-related disasters come with huge costs
August saw the formation of 19 named storms across the globe, with eight reaching tropical cyclone strength. Six of these storms, including two hurricanes, happened in the Atlantic Ocean — more than usual for the region.
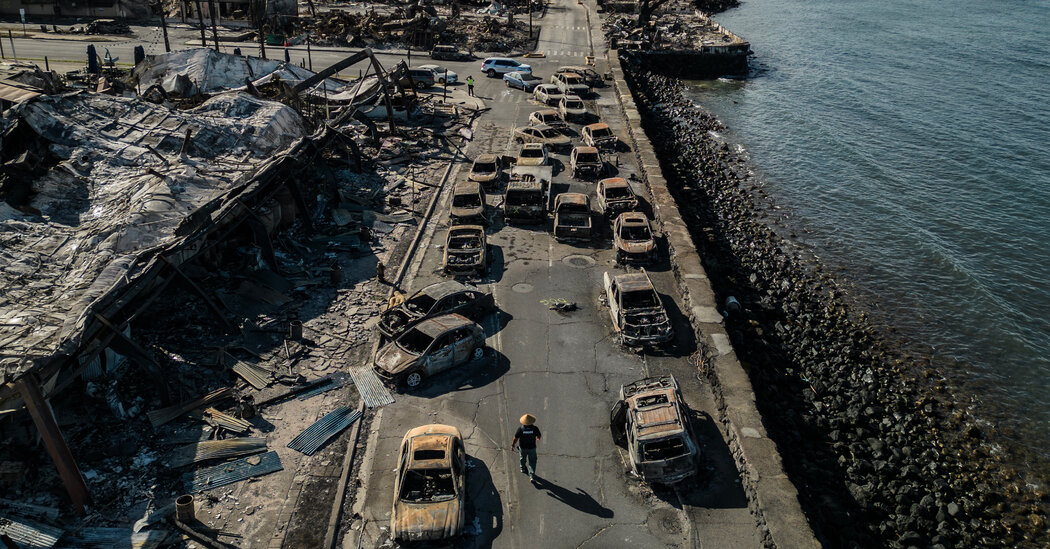
The United States has had 23 separate weather and climate disasters that cost more than $1 billion each in damages so far in 2023, the most ever in one year, even adjusted for inflation. These included the Category 3 Hurricane Idalia in Florida and the wildfires in Hawaii last month. The Maui wildfires were exacerbated by winds from Hurricane Dora and are believed to have killed 97 people. Southern California also had its first-ever tropical storm watch during Hurricane Hilary.
Background: Warmer temperatures fuel fewer but stronger storms
The effect of climate change on hurricanes is not straightforward. As wind patterns change, there may be slightly fewer tropical storms. But when storms do form, they will gather more energy from the hotter ocean and become stronger, sometimes over a single day or just a few hours. More hurricanes are likely to reach Category 3 or higher, as Idalia did.
What’s Next: Probably another record-breaking year
2023 will almost certainly be either the warmest or second-warmest year on human record, NOAA scientists said. El Niño conditions, which release additional heat into the atmosphere and are associated with warmer years on average, are expected to last at least through the end of the year.